Fat is one of the three main macronutrients, along with protein and carbohydrate. An important foodstuff, fats serve both structural and metabolic functions. Fats serve both as energy source for the body and as store for energy in access of what the body needs immediately. Each gram of fat when burned or metabolized releases about 9 calories of energy.
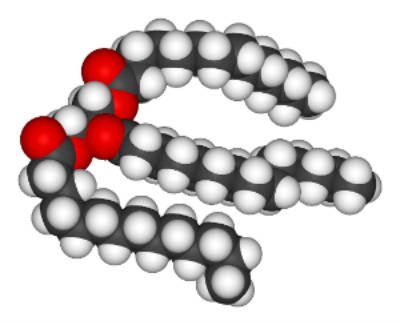
As shown in the image above, a fat molecule consists of a central glycerol portion to which three fatty acid chains are attached. Fats are broken down in the body to release their constituents, glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol is converted into glucose by the liver and serves as a source of energy.
Significance of Fats
Fats have always been feared to be someone who will cause increase in weight along with obesity. They have also been accused of being the mail culprit in causing heart related problems. Though this is true to certain extent, not all fats were created equal. Just like everything else in the world, some fats are good while others are bad. While bad fats increase the risk to certain diseases and ailments, good fats are vital to physical and emotional health. Some benefits include
- Since 60% of the brain is made up of fat, healthy fats are essential to brain development and function.
- Helps absorb fat soluble vitamins which are A, D, E and K
- Some good fats are beneficial for a healthy heart
- Useful for emotional well being and mood uplift
- Excellent source of energy
- Fats regulate the production of reproductive and steroid hormones, as well as genes involved in growth and metabolism
Types of Fats
Fats are of different types. Body makes its own fat by taking in access calories. Fats found in foods from plants and animals are known as dietary fats. Some fats are good while others are considered bad, depending upon whether they are beneficial or harmful for the health respectively. Let us see each one in detail.
Saturated Fat
This considered to be “bad” fat because consuming it in access increases the risk of heart disease. Saturated fat is solid at room temperature and comes mainly from animal sources of food like red meat, poultry and full fat dairy products like milk, cheese, butter and cream. They are also found in plant based sources like coconut oil, palm oil , cocoa butter and palm kernel oil.
Saturated fats are considered to be harmful as too much consumption of them can lead to increase in the level of cholesterol which increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Cholesterol in the body has two components : HDL (good) and LDL (bad). LDL builds up in blood vessels and causes them to be narrow which in turn increases the risk of blood clotting which increases the risk of heart attack. HDL on the other hand retrieves LDL from the body and transports it to the liver so that too much of it doesn't gets into the bloodstream.
Saturated fats increase the level of this “bad” component of cholesterol in the body. Following are the foods which are rich in saturated fats :
- Cakes, cookies and other grain based desserts
- Pizza and cheese
- Whole and reduced fat milk, butter and dairy desserts
- Meat products like sausage, bacon, beef and hamburgers
Though some recent studies have stated that there is not much correlation between saturated fat consumption and cardiovascular diseases, but it is definitely better to replace bad fat with good fat in the diet.

Trans Fats
This type of fat is made by a process called hydrogenation, where vegetable oils are heated in the presence of hydrogen gas and a catalyst. This process makes the shelf life of the fats longer and less likely to become rancid. Partially hydrogenated oils can withstand repeated heating without breaking down. Hence such fats are popular in hotel industry and used extensively for frying fast foods, baked foods and process foods which are consumed as snacks. They are also naturally found in small amount in meat and dairy products.
Trans fats are “worse” than saturated fats when it comes to health consideration. They increase the LDL component of cholesterol and lower the HDL. They create inflammation, which is accused of playing an important role in heart disease, stroke, diabetes and other chronic diseases. Following are the foods which are rich in Trans fats :
- Snacks like chips, crackers
- Processed foods
- Some spreads and salad dressings
- Cookies
- Food made with partially hydrogenated oils

Unsaturated Fats
Unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature. They are mainly found in oils from plants, nuts and seeds. They are considered to be “good” fats as they help improve blood cholesterol levels, ease inflammation and stabilize heart functions. Unsaturated fats are classified into two types :
Monounsaturated Fats (MUFAs)
They are mainly found in :
- Olive, peanut and canola oils
- Nuts like almonds, hazelnuts and pecans
- Avocados
- Seeds like pumpkin and sesame seeds
Polyunsaturated Fats (PUFAs)
They are mainly found in :
- Safflower, sunflower, soybean, sesame and corn oils
- Walnuts
- Flaxseeds
- Seafood especially fish
PUFAs are further classified into two broad categories
Omega-3 fatty acids
These are associated with good heart health as they decrease the probability of blood clotting and maintain healthy heart rhythm. They are also important during pregnancy and breastfeeding to support child development. Since the body can not manufacture omega-3 fatty acids, they must come from food. They are mainly found in :
- Oily fish like salmon, meckeral, sardines, herring, trout
- Plant oils like soybean oil, canola oil, linseed oil, sunflower oil
- Walnuts
- Flaxseeds
Omega-6 fatty acids
Along with omega-3 fatty acids, omega-6 fatty acids play a crucial role in brain function, normal growth and development. They help stimulate skin and hair growth, maintain bone health, regulate metabolism, and maintain the reproductive system. They are mostly found in liquid vegetable oils like soybean oil, corn oil, and safflower oil.

How much fats should be consumed
Adults should consume 20-25% of their daily calories from fat. Saturated fat should constitute less than 10% of the calories consumed. Apart from this, 250mg of omega-3 fatty acids on an average per day should be consumed.
BOTTOMLINE : Avoid trans fats and try to replace saturated fats with unsaturated fats in your diet.





